Once an enterprise has analyzed its mission and defined its goals, it needs a way to measure progress toward those
goals. Many things contribute to organization's success. Those that are key contributors such as Key Performance
Indicators (KPIs), also known as Key Success Indicators (KSIs) or Key Business Indicators (KBIs), are used by
businesses to define and measure progress toward their goals. In SOMA, KPIs represent quantifiable measurable
objectives, agreed to beforehand, that reflect the critical success factors of an organization.
KPIs differ depending on an industry and an organization. A sales organization may have as one of their KPIs
the percentage of its sales that comes from return customers. A Customer Service Organization may have a KPI that
measures a number of customer calls answered in under a minute. To determine if the objectives associated with a
KPI are being met, the KPI may need to be broken down into one or more metrics, which identify specific
measurements to collect for analysis (e.g. time to close an average sale deal).
The purpose of this step is to define how the Business Goal will be measured by identifying at least one
KPI and hopefully the corresponding metrics for each goal and sub-goal. If you can find a quantitative measure to
assess whether or not the business goal has been achieved, the business goal probably can be related to business
activities. KPIs will provide the business with a measure of success of meeting its goals and sub-goals. For
example, for a goal of "increase revenue", a KPI could be "increase revenue by 5% during the next fiscal year" - this
provides a specific way to determine if the goal has been met. Metrics identify the type of measurements that need to
be collected to assess the state of the KPIs. For a example KPI above, a metric could be "record the revenue from
all revenue generating transactions".
Try to quantify the expected outcome and record this in the change value and change kind properties of the business
goal. Because people often set more ambitious goals for themselves than others would, it is useful to discuss the upper
and lower boundaries with those responsible for achieving the business goal. Employees need to feel that there is
enough challenge in their work, but they also like to be able to give themselves an occasional pat on the back.
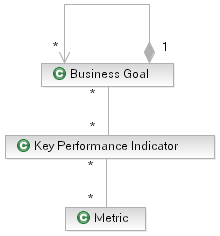
As described in the Guideline: Business Goal the relationship between Business Goals, KPIs and Metrics can be seen in the following diagram.
If the measure is qualitative or subjective, the business goal may need to be translated to more measurable, sub-goals.
In this case, the sub-goals are identified by considering how the higher-level goal will be measured. It is important
that all leaf-level goals have identified KPIs. Achievement of some or all of the sub-goals should result in
achievement of the higher-level goal. If a business goal has been assigned a date by which it should be achieved, it is
sufficiently concrete to be called an objective. When determining the timeframe within which the goal is to be
achieved, be ambitious yet realistic.
|

